
Precision casting with excellent quality
Integrated research and development, manufacturing, sales, and technical services of laboratory scientific instruments and intelligent equipment
National Consultation Hotline 15738867410

Integrated research and development, manufacturing, sales, and technical services of laboratory scientific instruments and intelligent equipment
National Consultation Hotline 15738867410
15738867410
Greenland Binhu International City (District 1), Erqi District, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province
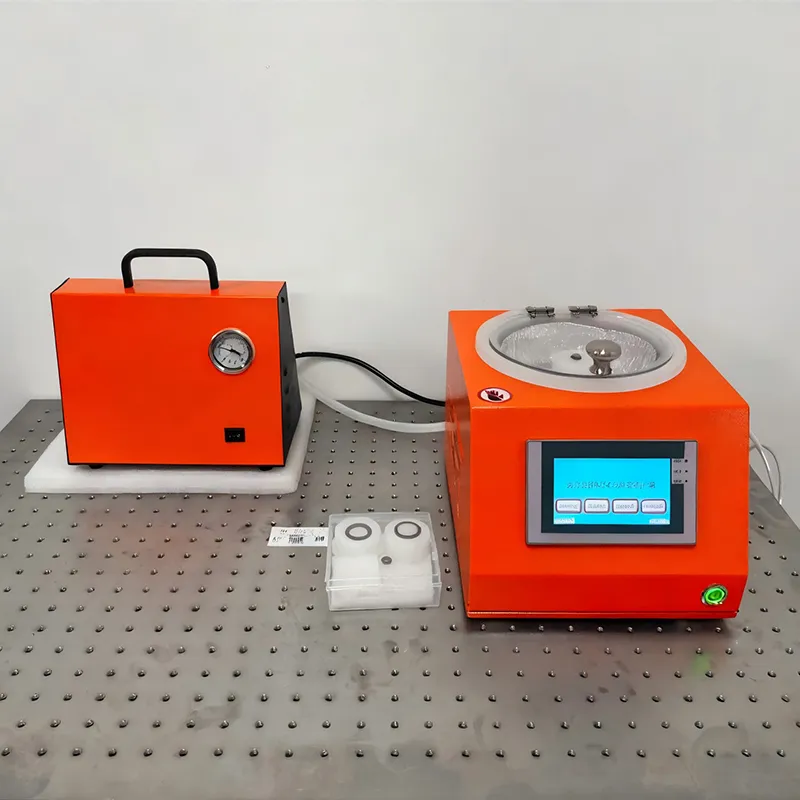
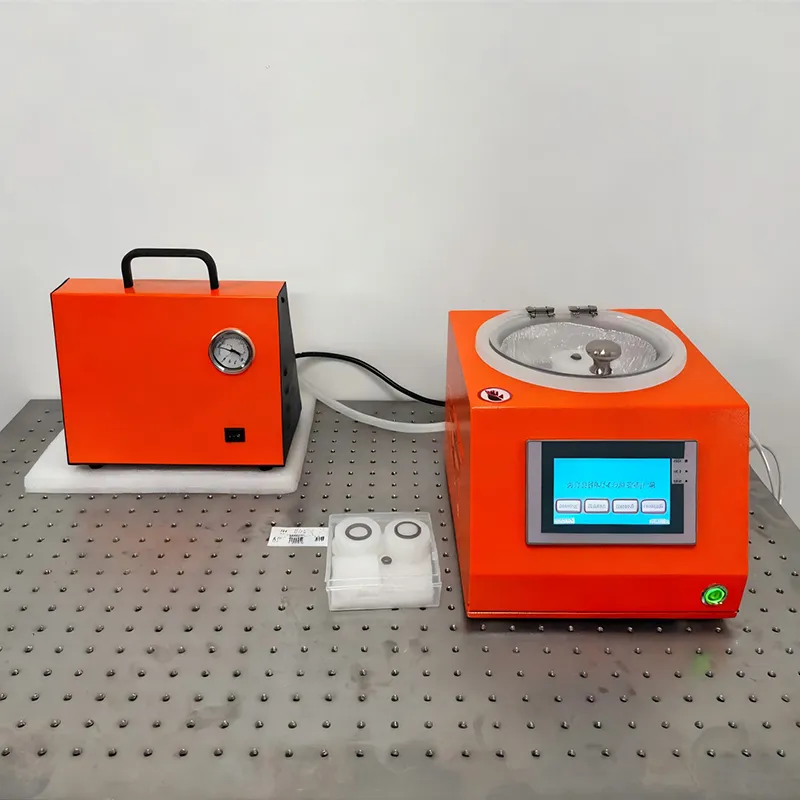
Details
Intelligent glue spreading machine
Product Description
The equipment commonly used in spin coating technology is a spreader. Spin coaters have many names, including SpinCoater or Spin Processor in English, also known as glue machine, spin coater, spin coater, spin film coater, spin coater, spin coater, spin film machine, spin coater, spin coater, spin film machine, spin coater, spin coater, and film spreader. Generally speaking, their principles are the same, that is, various types of glue are dripped onto the high-speed rotating substrate, and the centrifugal force is used to evenly coat the glue dripped on the substrate. The thickness varies depending on the viscosity coefficient between the glue and the substrate, and is also related to the rotation speed and time. The speed range is 0-9999rpm and the spread size is 8mm-20cm.
The principle of glue spreader
Spin coaters are no strangers to researchers working in the field of microfluidics. They can be used to prepare thin films with a thickness of less than 10nm and are often used in photoresist deposition processes with a thickness of 1-100um. In the field of microfluidics, glass slides, silicon wafers, ITO conductive glass, etc. can all be used as substrate materials for thin film coating . The principle is simple: negative pressure is generated by the wafer holder, and the substrate material to be spin-coated is adsorbed on the wafer holder. The spin-coating material glue is then dripped onto the surface of the substrate material. By adjusting the motor speed to change the centrifugal force, the glue flow rate is controlled at the same time to obtain the desired film thickness. Of course, the film thickness is also related to factors such as spin coating time, glue viscosity, temperature, and humidity.
Parameters related to the performance of the glue machine
(1)Sheet support material: Currently, most sheet supports of glue spreaders are generally made of aluminum alloy or ordinary plastic. The reason is low cost and can meet general requirements. However, for industries with more stringent requirements, such as semiconductor and chemical industries, the corrosion resistance of aluminum alloy is not very good, and high temperature and high pressure will cause plastic deformation. Therefore, the requirements for sheet supports are relatively high. Currently, natural polypropylene and polytetrafluoroethylene are generally used . The reason is that these two materials have the advantages of green and environmentally friendly materials, light weight, high strength, durability and good impact resistance.
(2)Vacuum adsorption and cleaning system: The vacuum pump system pressure must be accurately calibrated. If the actual pressure is too low, flying flakes may occur, which can easily lead to experimental accidents. After using the spin coater, it is necessary to open the spin coater and clean the pores with an organic solvent to ensure normal use next time.
(3)Rotation speed: The speed and precision control will directly affect the thickness and uniformity of the spin coating. Therefore, the error between the indicated speed and the actual speed of the motor must be minimized, otherwise the user will not be able to obtain useful experimental data.
What operating behaviors can affect the thickness of the spin-coated coating?
(1) Glue drops are injected onto the surface of the base material. The amount of glue drops must be much larger than the glue liquid that is finally coated on the surface .
(2) The film thickness can be changed by changing the substrate rotation speed at a constant time.
(3) Rotating the substrate at a constant rate and duration can affect the film thickness through the volatility of the glue.
(4) Through rapid acceleration, the substrate speed quickly reaches the set ideal speed.
(5) Keeping the spin coating rate constant, the film thickness can be changed by changing the substrate spin coating time.
(6) Maintaining a constant speed and substrate rotation time, the film thickness can be changed by changing the viscosity of the glue.
Introduction to the coating process:
A typical coating process includes the following steps: coating, high-speed spinning, and drying (solvent evaporation). The coating step involves dripping the photoresist onto the substrate surface. High-speed spinning spreads the photoresist onto the substrate to form a thin layer. The drying step removes excess solvent from the coating. Two common coating methods are static coating and dynamic coating.
Static dispensing involves simply dripping photoresist onto the center of a stationary substrate surface, with the amount of dispensing varying from 1 to 10 mL . The amount of dispensing depends on the viscosity of the photoresist and the size of the substrate. For higher viscosities or larger substrates, a larger amount of dispensing is often required to ensure that the entire substrate is coated during high-speed rotation.
Dynamic dispensing involves dispensing the photoresist while the substrate is rotating at a low speed (usually around 500 rpm). This " dynamic" process allows the photoresist to spread more easily across the substrate, reducing waste. Dynamic dispensing eliminates the need for a large amount of photoresist to wet ( cover ) the entire substrate surface. This method is particularly effective when the photoresist or substrate itself has poor wettability, preventing the formation of pinholes.
After dispensing, the next step is high-speed spinning. This thins the photoresist layer to the desired final thickness . The rotational speed at this stage is generally between 1500 and 6000 rpm. The speed selection also depends on the photoresists properties (including viscosity, solvent evaporation rate, solids content, and surface tension) as well as the size of the substrate. High-speed spinning can last from 10 seconds to several minutes. The speed and time of the spin coating process often determine the final film thickness.
Generally speaking, faster spin speeds and longer spin times result in thinner films. Numerous variables influence the spin coating process, and these factors often counteract each other and reach equilibrium during the process. Therefore, its best to allow sufficient time for the spin coating process to achieve equilibrium among these factors. Repeatability is paramount in the spin coating process; even subtle variations in process parameters can lead to significant differences in film properties.



QR code

Contact information
15738867410
Online Message
Top